About Virus:
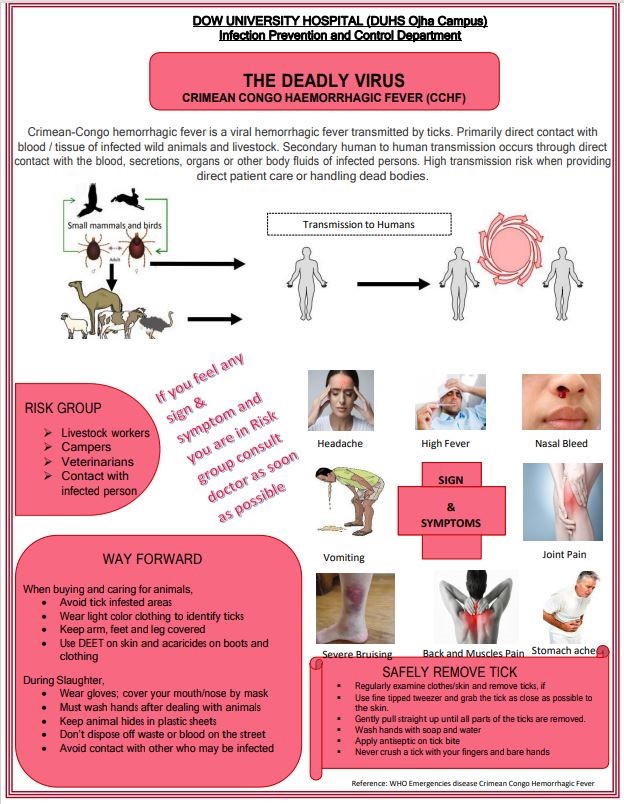
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever (CCHF) is a viral disease that can cause severe illness and, in some cases, death. It is transmitted to humans through ticks and direct contact with the blood or bodily fluids of infected animals or people. As awareness plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, this post aims to provide essential information about CCHF to help you stay informed and take necessary precautions.
Key Facts about CCHF:
Transmission: CCHF is primarily transmitted through ticks, particularly the Hyalomma genus, found on domestic and wild animals. It can also spread through contact with infected blood, tissues, or bodily fluids of humans or animals.
Geographical Distribution:
CCHF occurs in many countries across Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. Regions with a high risk of CCHF include parts of Africa (particularly sub-Saharan Africa) and Central Asia.
Symptoms:
The onset of CCHF is usually abrupt and includes fever, muscle aches, dizziness, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In severe cases, it can progress to hemorrhage, organ failure, and death.
Prevention:
Preventive measures include avoiding tick bites, wearing protective clothing, using insect repellents, and maintaining good hygiene practices. It is also crucial to avoid contact with blood or bodily fluids of infected individuals or animals.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment. If you suspect CCHF, seek medical attention immediately. There is no specific antiviral treatment available, but supportive care and timely medical intervention can improve outcomes.
Precautionary Measures:
Tick Bite Prevention:
Use insect repellents containing DEET on exposed skin and clothing.
Wear long sleeves, pants, and socks in areas with high tick activity.
Conduct regular tick checks after spending time outdoors and promptly remove any attached ticks.
Hygiene Practices:
Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling animals or potentially contaminated materials.
Use protective gloves and appropriate gear when in contact with potentially infected individuals or animals.
Animal Handling:
Avoid contact with blood, tissues, or bodily fluids of animals, particularly if they appear sick or have died suddenly.
Implement proper animal husbandry practices and seek veterinary assistance if animals display unusual symptoms.
Healthcare Precautions:
Healthcare workers should follow infection control protocols and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when treating suspected or confirmed CCHF cases.
Isolation measures should be implemented to prevent the spread of the virus.
Stay Informed and Spread Awareness:
Share accurate information with family, friends, and the community to raise awareness about CCHF and its prevention.
Educate yourself about the symptoms, transmission, and preventive measures associated with CCHF through reliable sources such as healthcare organizations and official health websites.
Remember, by staying informed, adopting preventive measures, and promoting awareness, we can collectively combat the spread of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever. Let’s prioritize our health and safety!